About Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a gram-negative curved rod or s-shaped bacterium that infects the gastric mucosa3
First discovered in 1982 by Warren and Marshall, it was later classified as a ‘carcinogen’ by the World Health Organization in 19945,6

H. pylori infection appears to be acquired throughout life, but commonly starts in infancy7
Routes of H. pylori transmission include:7
- Faecal-oral
- Oral-oral (dental)
- Gastro-oral
- Sexual behaviour
Once a person acquires H. pylori infection, the bacteria usually persists throughout their lifetime3
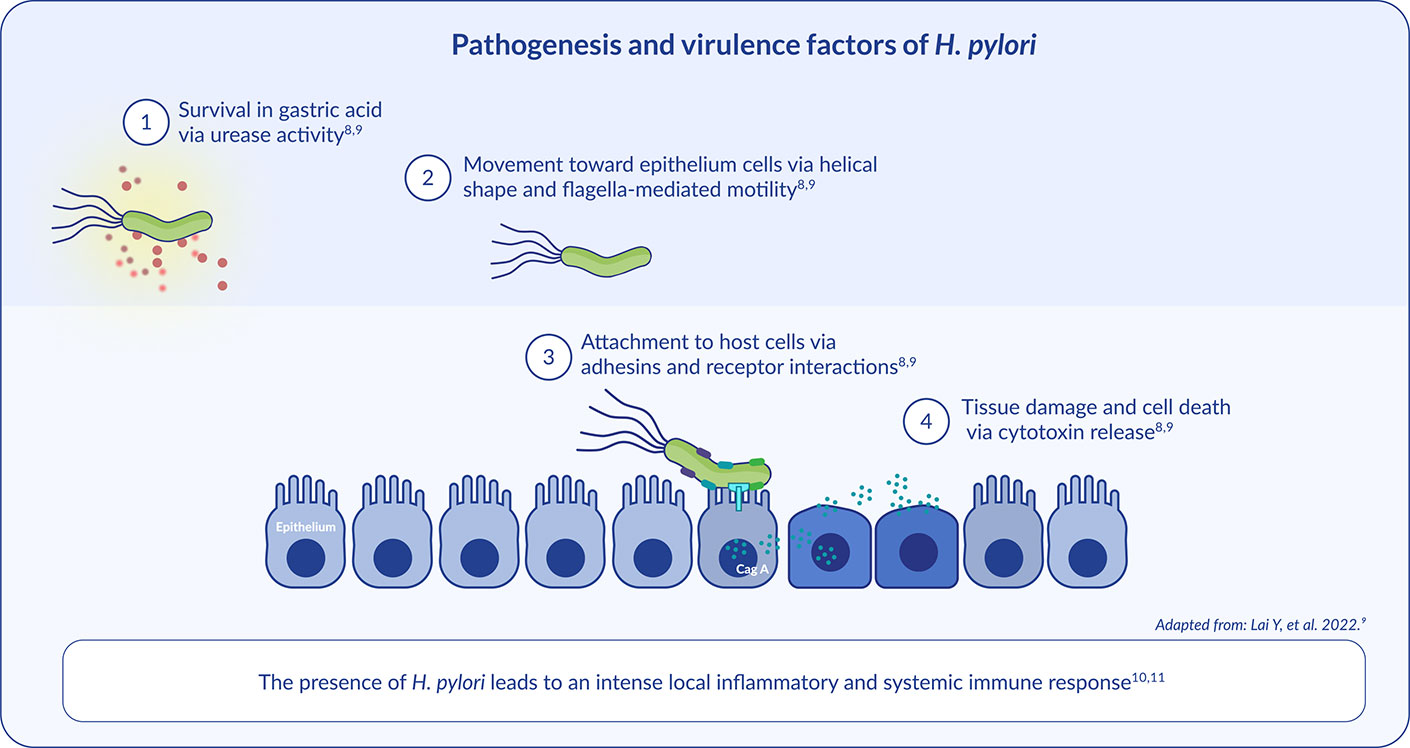
After entering the host stomach, four critical steps occur to establish successful H. pylori colonisation, persistent infection, and disease pathogenesis:8,9
Worldwide impact
Almost 50% of adults are infected by H. pylori worldwide1
H. pylori remains a major global health problem13
Consequences of infection
H. pylori-associated gastritis is the underlying cause of almost all gastric diseases19
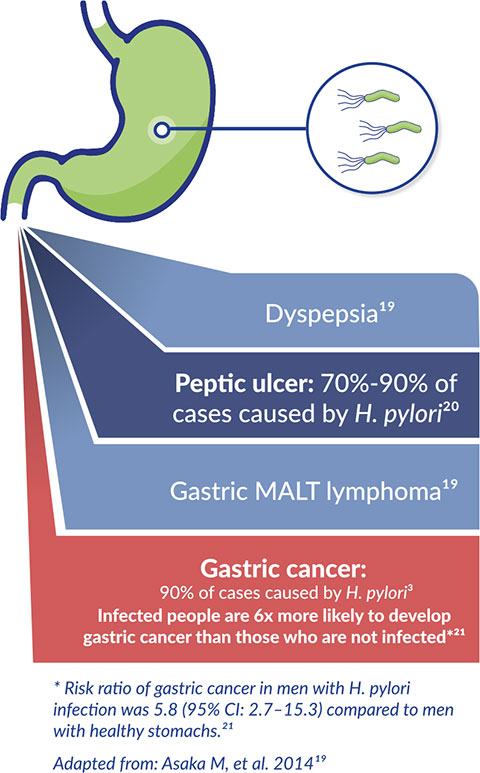
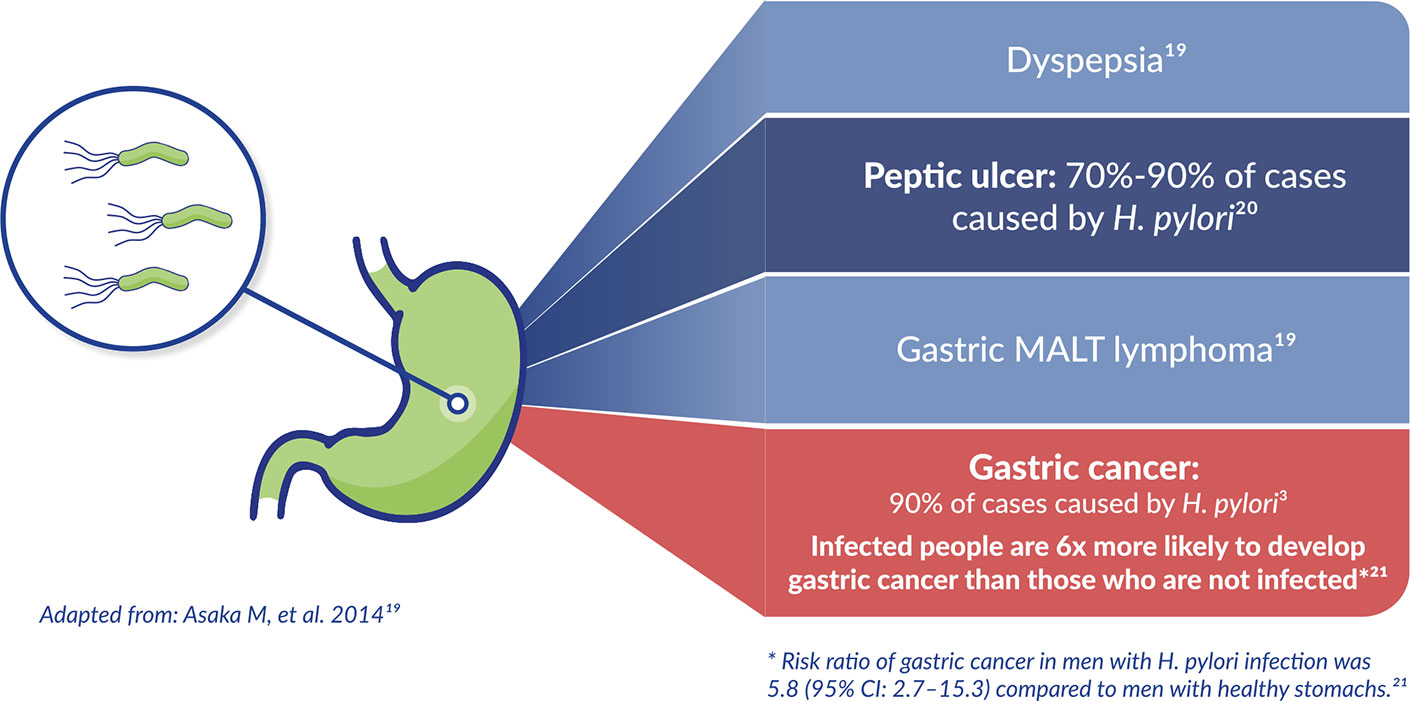
Extra-gastric diseases also associated with H. pylori infection:3
- Unexplained iron deficiency anaemia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (in some instances)
H. pylori symptoms
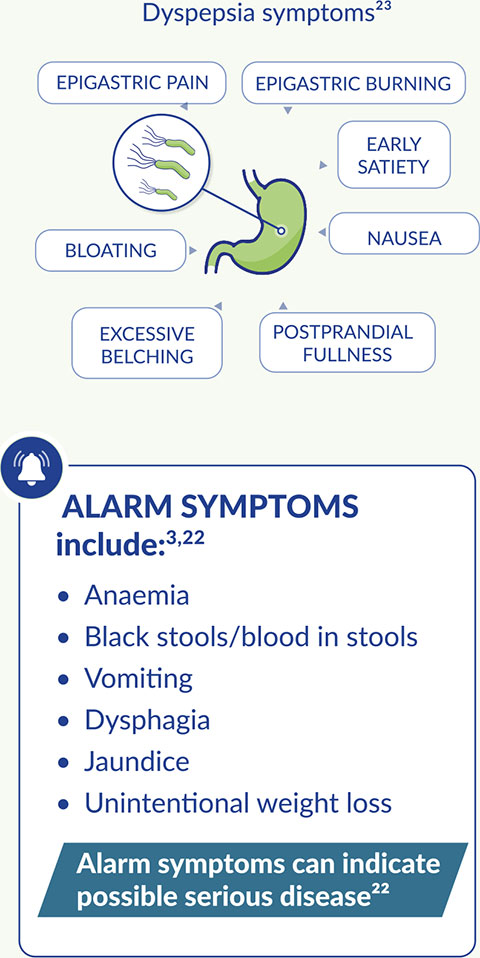
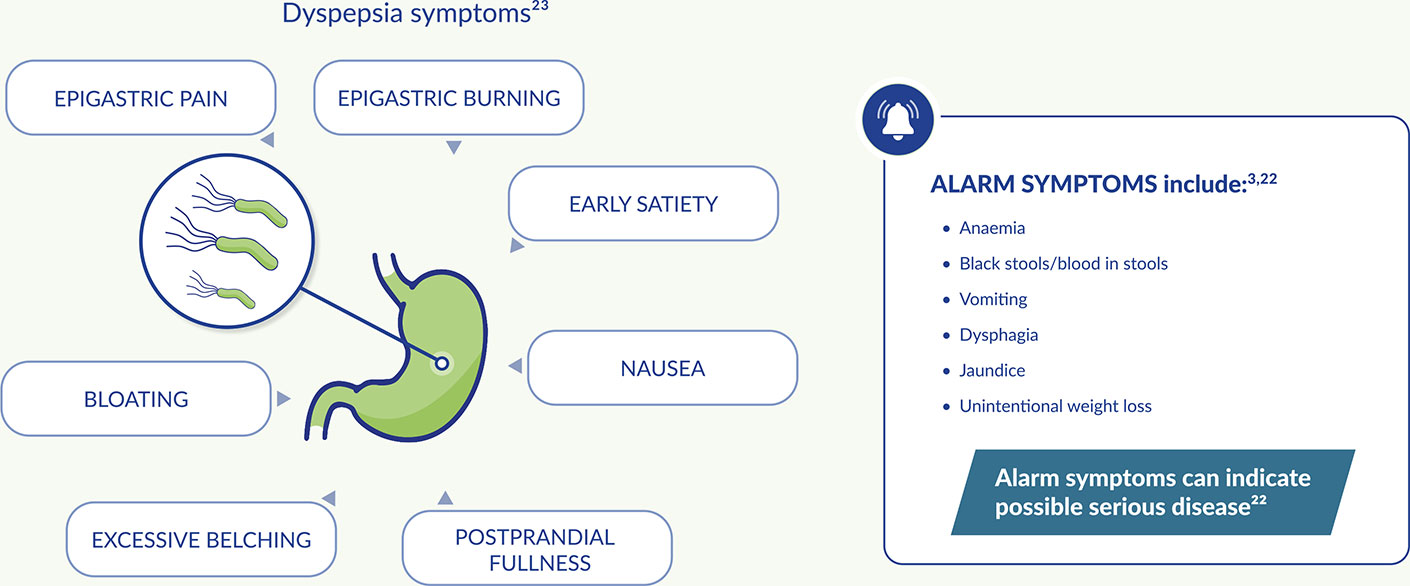
The symptoms of H. pylori can include alarm and non-alarm symptoms3,22
Which patients should be tested?
According to international guidelines, the following patient profiles should be investigated for H. pylori3,4
Dyspeptic patients with or without alarm symptoms
- Patients with a family history of gastric cancer
- Patients with a history of endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer
- Patients with low-grade gastric MALT
Patients with long-term PPI use
- High risk patients already on long-term aspirin
- Naïve patients starting long-term NSAID therapy
Immigrants from areas with a high prevalence of H. pylori infection
- Patients with iron-deficiency anaemia when other causes have been excluded
- Adult patients with immune thrombocytopenia
Patients with active or history of peptic ulcer disease
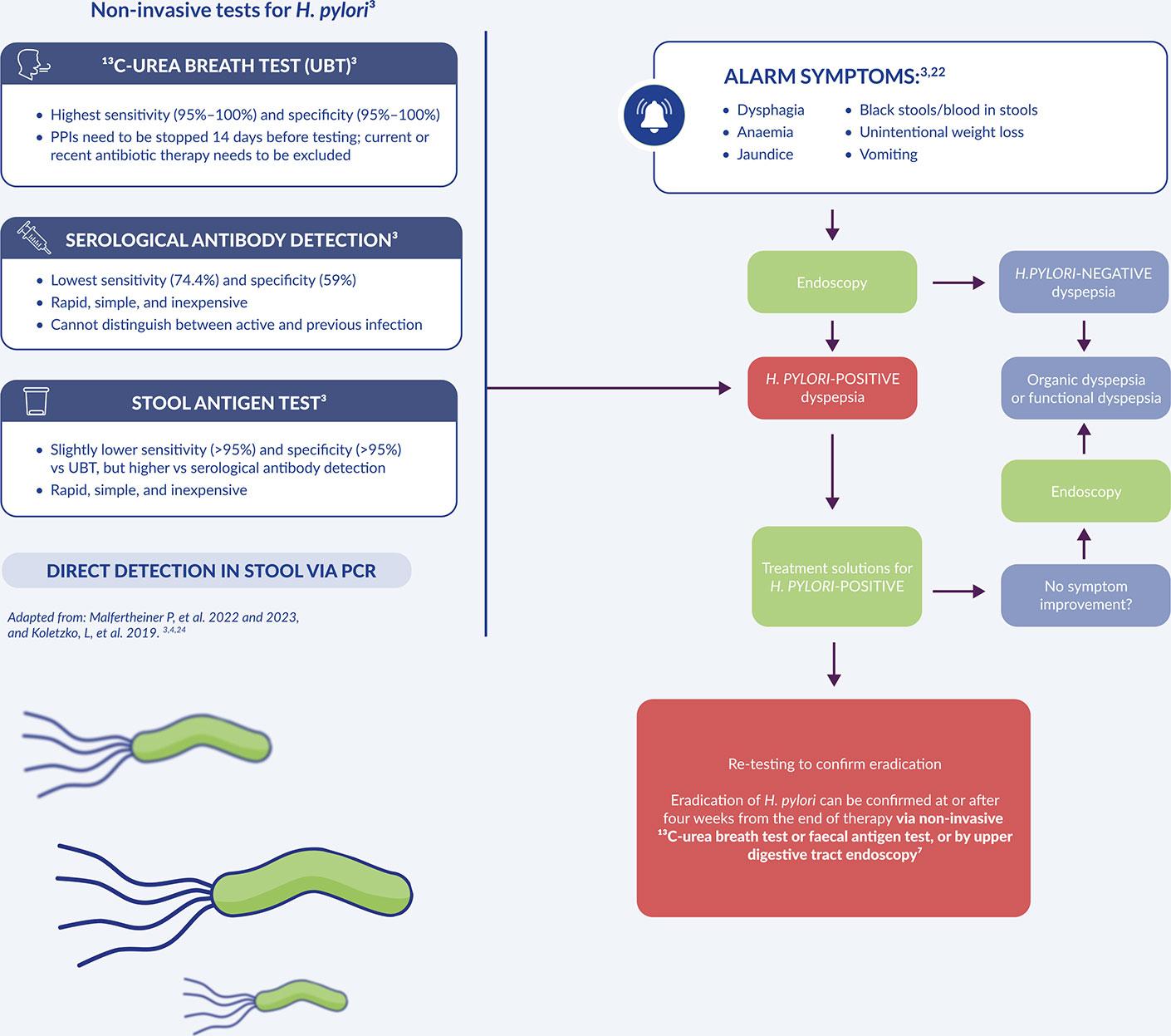
Testing methods
Patients aged <50 years with dyspepsia3,4
Patients aged ≥50 years with dyspepsia or at any age with ALARM SYMPTOMS3,4
For your clinical practice
Explore our resources to help with your clinical practice